The Grand Aquarium de Touraine is concerned with biodiversity and its conservation. Discover the agreements that ensure the sustainability of animal species.
In order to present live wildlife to the public, France has introduced the "certificat de capacité" to regulate the exhibition of these animals. Within this framework, each establishment must have a "capacitaire", a qualified person recognised by the prefecture and the Ministry of the Environment.
The Grand Aquarium de Touraine presents hundreds of different species of aquatic animals. Among those you can observe, some are considered endangered.
In order to learn more about the protection status of animals, here are the 3 main benchmarks to learn more about the level of threat of species:
The Washington Convention or CITES
This is an international treaty on trade that came into force in 1975. It has 175 member countries.
This convention concerns endangered wildlife. It regulates the trade in species to ensure their survival. It concerns living animals and plants, but also all products derived from them (shells, carapaces, wood, furs, skeletons, etc.).
Species are classified in three appendices according to their level of threat in order to indicate to what extent they can be exploited and traded.
Appendix I: this includes species threatened with extinction. Trade in these species is totally prohibited except, with agreement, for scientific research or population management.
Annex II: contains species whose conservation status or overexploitation may threaten their survival. These species may be traded but with a tracking number and full traceability.
Appendix III: this lists the species whose trade the member countries of the Convention wish to regulate. It is a kind of waiting list before moving to Appendix I or II or, by chance, leaving the Convention.
IUCN
This is the International Union for Conservation of Nature. It was founded in 1948.
It is an international NGO made up of scientists and wildlife enthusiasts.
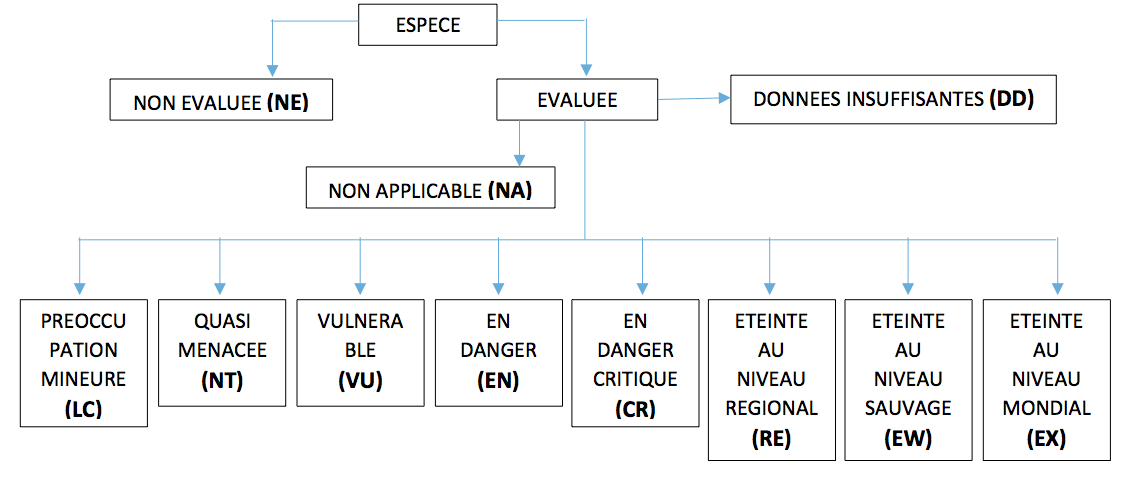
Its role for animal and plant species is to inform, encourage, assist and influence different countries to conserve species by publishing a red list. This list is updated regularly and can be consulted on the website. It lists the endangered species in the world. The degree of danger is established according to observations and long-standing scientific data.
Here is a diagram of the different levels used to classify species in the Red List.
The Bonn Convention or CMS
This is a convention on the conservation of migratory species of wild animals, which came into force in 1983.
It is divided into 2 appendices:
Annex I: this lists the species in danger of extinction. All taking of these species is prohibited.
Annex II: lists species whose conservation status is unfavourable. For these species, measures must be implemented to restore the good status of the populations.